Inflammatory Bowel Disease or IBD is a medical term used to describe the disorders of chronic inflammation of the digestive tract of an individual. There are two types of IBDs mentioned below:
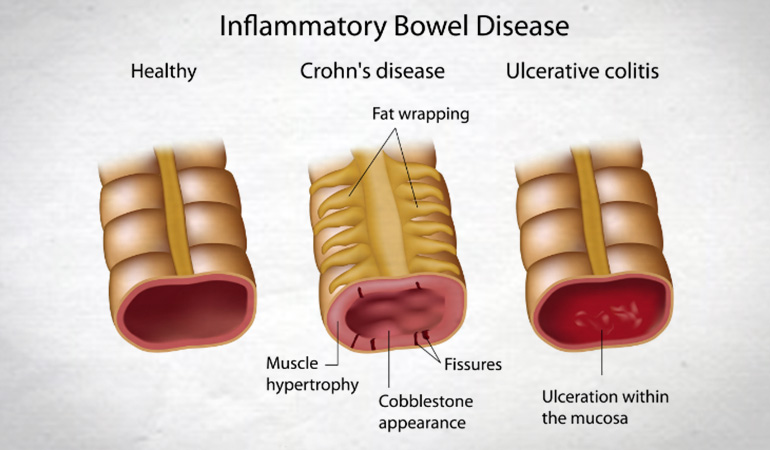
Ulcerative Colitis- Ulcerative colitis is caused due to inflammation and sores in the innermost lining of the large intestine for a long time.
Crohn’s Disease- Crohn’s Disease is the inflammation of the inner lining of the digestive tract. This disease often spreads deep into the tissues of the affected areas.
Both these diseases are accompanied by severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and abdominal pain. IBD can cause a lot of weakness in the patient and can also lead to fatal conditions. If left untreated, the disease grows and spreads.
IBD is a serious disease that can get worse if not treated on time. Consult a doctor if you observe abnormal changes and symptoms indicating falling health. In the case of IBD, the patient observes changes in bowel movement. The body shows symptoms of the disease since the beginning. If it gets worse, consult your doctor.
Ulcerative Colitis- Ulcerative colitis is caused due to inflammation and sores in the innermost lining of the large intestine for a long time.
Crohn’s Disease- Crohn’s Disease is the inflammation of the inner lining of the digestive tract. This disease often spreads deep into the tissues of the affected areas.
Both these diseases are accompanied by severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and abdominal pain. IBD can cause a lot of weakness in the patient and can also lead to fatal conditions. If left untreated, the disease grows and spreads.
Symptoms
The symptoms of IBD vary and depend upon the type and extent of the disease. The disease can have mild symptoms in the early stages of the disease and can also have complicated and severe symptoms in the serious stages of the disease. Common symptoms of IBD include:- Severe Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- High Fever
- Cramps
- Abdominal Pain
- Blood in stool or toilet paper
- Loss of appetite
- Sudden weight loss and anemia
- Bloating and stomach pain because of obstruction in bowel movements.
- Bleeding ulcers.
- Arthritis.
- Eye inflammation
- Skin Disorders
- Ulcers or fissure around the anal area or private parts.
IBD is a serious disease that can get worse if not treated on time. Consult a doctor if you observe abnormal changes and symptoms indicating falling health. In the case of IBD, the patient observes changes in bowel movement. The body shows symptoms of the disease since the beginning. If it gets worse, consult your doctor.
Causes of IBD
There is not one single cause factor that leads to the disease of IBD. The early studies claimed stress and unhealthy diet as the reasons for IBD but with time, it came to light that these two factors play an important part in making the disease worse but are solely not responsible for the disease.
The exact and accurate cause of the disease is unknown. But malfunctioning of the immune system of the individual is suspected to be one of the major possible causes. The immune system has the role to defend the body of the individual against disease and infection-causing pathogens. Presence of any sort of bacterial or viral infection in the digestive tract can fire off the immune response. The body's attempt to fight with the foreign pathogens can lead to inflammation of the digestive tract itself. The inflammation goes off on its own after the infection is gone. A person suffering from IBD can have the infection of digestive tract anyway, even if there is no infection prevailing. IBD can also happen in cases where the inflammation does not cure on its own and carries off for several months or years.
The patient is then advised to get the Stool and blood tests for more accuracy on the disease. The blood test is done to identify if the patient has Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis. But the blood tests all over cannot be used to diagnose IBD.
The doctor then suggests for further tests to identify the extent and spread of the disease.
Medication or Drug Therapy- In the early stages of the disease, the medication can provide a cure for the disease. However, if the disease has escalated to a severe condition, the surgery might be the only solution to help the patient get relief.
There are some effective medications that get give relief from the inflammation in the inner lining of the intestines. The patient may need antibiotics to prevent infections in the case of Crohn’s disease. The doctor may prescribe other medications such as anti-diarrheal medicines, pain killers, iron supplements, calcium and vitamin D supplements, etc.
If the patient gets no relief with the medication, Laparoscopic surgery is performed to give permanent relief from this disease.
Risk Factors Involved
- Smoking- Smoking is considered to be one of the biggest risk factors leading to Crohn’s Disease. Smoking triggers the pain and symptoms of IBD and also increases the risks and complications of the disease. Controlling this risk can somehow prevent this disease.
- Age- A huge majority of the people diagnosed with IBD are till 30 years of age. But there are also diagnosed with IBD on their 50s or so.
- Genetic Factor- If IBD has been a problem for people in your family, especially the same or previous generation, one is more likely to have this disease.
- Geographical Area- IBD is a more common disease in urban and industrialized areas. People working in corporate jobs have a high risk of developing IBD, main reason contributing to it is the diet and lifestyle choices. Eating junk, oily and processed food in excess contributes to the risk factors.
- Complications due to Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Malnutrition
- Weight Loss
- Colon Cancer
- Fistula
- Anal Fissure
- Intestinal Rupture
- Obstruction in normal bowel movements.
- Blood Clots
Diagnosis of the Disease.
After hearing the general symptoms, the doctor can recognize if the patient has IBD. There are certain tests done in particular to check for the cases of IBD. The doctor firstly confirms if the disease has previously occurred to anyone in the family. The doctor also confirms if there is the case of bowel diseases in the family’s history. The doctor also enquires about the bowel movements of the patient.The patient is then advised to get the Stool and blood tests for more accuracy on the disease. The blood test is done to identify if the patient has Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis. But the blood tests all over cannot be used to diagnose IBD.
The doctor then suggests for further tests to identify the extent and spread of the disease.
Effective Treatments for IBD?
In most cases of IBD, the medication itself can cure the inflammation and other symptoms. It may also reduce the complications and risks associated with the disease. There are two options available for the IBD treatment, Medication or Surgery. Both of them are briefed below:Medication or Drug Therapy- In the early stages of the disease, the medication can provide a cure for the disease. However, if the disease has escalated to a severe condition, the surgery might be the only solution to help the patient get relief.
There are some effective medications that get give relief from the inflammation in the inner lining of the intestines. The patient may need antibiotics to prevent infections in the case of Crohn’s disease. The doctor may prescribe other medications such as anti-diarrheal medicines, pain killers, iron supplements, calcium and vitamin D supplements, etc.
If the patient gets no relief with the medication, Laparoscopic surgery is performed to give permanent relief from this disease.




0 Comments